
In the actual application of RFID, the electronic tag is attached to the surface of the object to be identified, and the electronic data in the agreed format is stored in it. The reader can read and identify the electronic data stored in the tag non-contact, so as to achieve the purpose of automatically identifying the object.
The reader sends a radio frequency signal of a certain frequency through the antenna. When the tag enters the magnetic field, it generates an induced current to obtain energy, and sends out its own coded information, which is read and decoded by the reader and sent to the host computer for related processing. RFID technology can complete the collection and transmission of item information without manual intervention.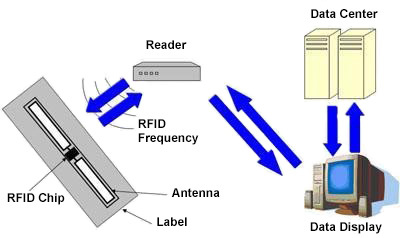
Internet+ refers to a new business format developed by the Internet under the impetus of Innovation 2.0 (information age, the innovative form of the knowledge society), and it is also a new form of economic and social development promoted by the evolution of the Internet form and spawned by the knowledge society innovation 2.0.
Simply put, Internet + is "Internet + traditional industry". With the development of science and technology, the use of information and Internet platforms enables the integration of the Internet and traditional industries, and uses the advantages and characteristics of the Internet to create new development opportunities.
With the help of the concept of Internet +, more traditional industries can be empowered through RFID technology, so that these industries can be more efficient and low-cost in the production process. In layman's terms, this + can be divided into two levels: one is to increase added value or improve efficiency and reduce costs for other industries; the other is to extend the RFID technology to more fields, so as to allow more The field can enjoy this technology.

RFID is not a panacea. Some solutions cannot be solved by RFID technology alone. Therefore, it is necessary to combine other technologies, such as AI technology, industrial vision technology, etc., and the ultimate goal is to solve the problem.
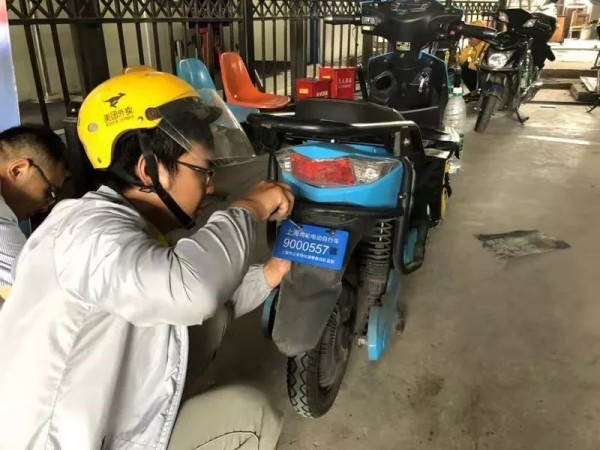
For example, the Shanghai electric vehicle management pilot case: One is the "electronic" number plate, which replaces the original electric vehicle number plate by installing an embedded RFID number plate on the electric vehicle, and collects relevant information of the vehicle and the owner during the registration process; The second is collection equipment, which collects the driving trajectory of electric vehicles in real time by deploying fixed collection equipment in areas with high incidence of electric vehicle traffic violations, so as to determine whether there are traffic violations; the third is video assistance, except for the use of RFID to collect traffic violations of electric vehicles. In addition to the driving trajectory of the city, combined with road video monitoring equipment, assisting RFID-collected illegal data of electric vehicles to carry out off-site law enforcement; fourth is the data cloud, through the establishment of a proprietary data cloud, to gather the city’s basic data of electric vehicles and carry out management work.

With the diversified development of application scenarios, simple identity collection can no longer meet the needs of the scenario. We can make RFID+ more sensing functions, such as temperature, humidity, torque, etc., to cope with the solution of smart scenarios.
For example, in a high-precision equipment operation and maintenance system, the operation of key components of the equipment can be monitored through RFID tags with sensor functions, and the wear level of vulnerable parts can be collected and uploaded in real time to make predictions to avoid major failures.

According to statistics, in recent years, the global annual shipment of RFID tags is about 20 billion, and applications in shoes, clothing, books, and aviation account for most of the usage. Then why is there so little use of RFID tags in other fields? When will it be as popular as barcodes and QR codes?
In fact, there are several reasons that affect the consumption of RFID tags: the high cost of tags, the greater the impact of environmental interference, the use of materials that are not environmentally friendly, and so on.
The localization of chips, the development of environmentally friendly antennas, and the development of tags to adapt to more complex environments require a variety of surrounding sciences to solve together. Whether it is material science, precision manufacturing science or process science, it needs to be explored and developed.

As the saying goes, "interlaced is like a mountain." Especially when the system integrator is doing application development, Party A will often deify the RFID function: "Can you use it as a monitor? With this, you can do everything and so on."
In fact, when making application solutions, RFID tag testing and selection, hardware development, and system software construction are not difficult. In the face of science, it is nothing more than okay or not. Of course, you must also consider how much Party A will pay to do this. The difficulty lies in fully understanding an industry, figuring out the business process of this industry, the pain points in the process, and how we can perfectly integrate RFID technology to solve the pain points and create value for Party A.
The success of RFID+ is to allow RFID technology to penetrate into people's daily life, work and other social activities, and to allow these users to feel natural and convenient in the process of use.


